Materials¶
The materials schema contains information regarding the materials that are used within components. These maybe a single base material from the materials catalogue and a combination of materials.
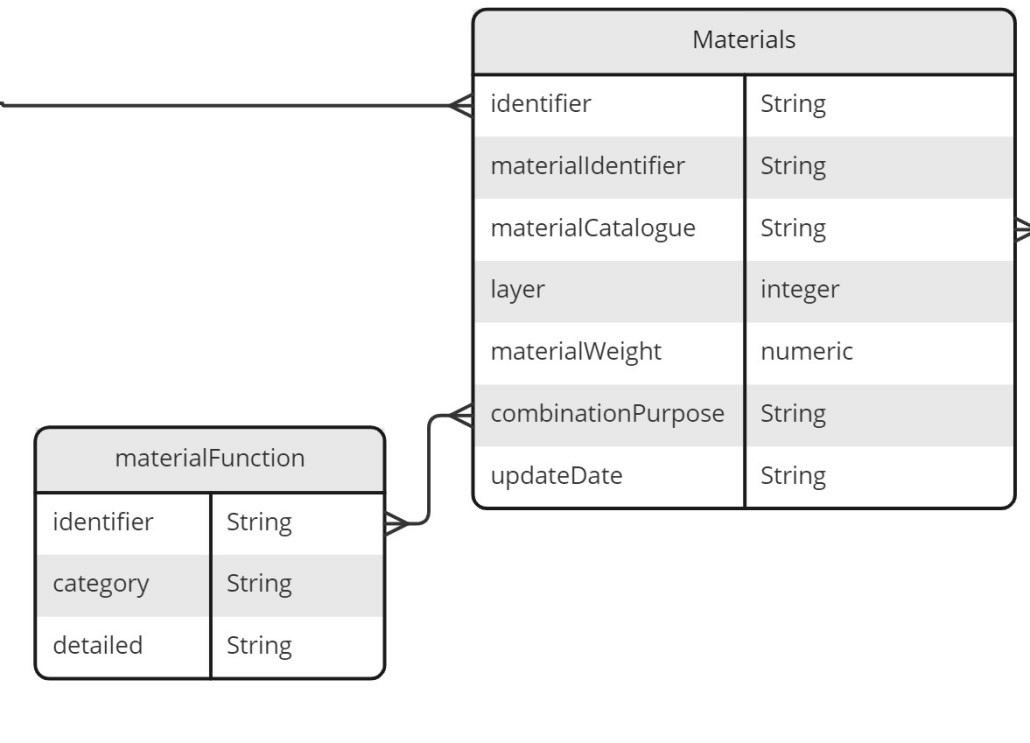
Table¶
| Column | Status |
Format | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| identifier | required |
String | A globally unique identifier. See identifiers section for information on how to construct this identifier |
| materialIdentifier | required |
String | The unique identifier of the created materials. See identifiers section for information on how to construct this identifier. |
| materialCatalogue | required |
String | The unique identifier of the material that this row relates to. There must be an equivalent record in the material_Catalogue data |
| layer | recommended |
integer | The layer associated with the component. The inner most layer (the layer closest to the product) denoted as 1, and the outermost layer is the biggest number. |
| materialWeight | recommended |
numeric | The percentage of the total materials making-up the component. For every unique componentCatalogue, weightMaterial should add to 100%. |
| combinationPurpose | recommended |
String | Why is this material being used? Use the identifier of the material function that this row relates to. The entry here should be drawn from the material function controlled list. |
| updateDate | required |
String | The date that the material was provided/last updated. Use the format dd/mm/yyyy. |
Diagram¶
Template¶
Materials should be provided as a separate csv file, in tidy format. This means that each row of the csv file should be one material for a component. An example is provided.
The specification of this csv file is as follows:
Example¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
Guide for how to take measurements¶
Units¶
All measurements should be given using the metric system.
- Weight: grams (g)
Numbers should be entered with a decimal place. Use the decimal / full stop / period character as a separator. Do not exceed 3 decimal places. When rounding, use convential rounding methods: for 5 and above round up, 4 and below round down. For example: volume = 0.67952 rounded to 0.68.
Important: When converting between systems of measurement, perform the conversion first and then apply the convential rounding. This will give more accuracy and consistency.